Description
- Construct Hadoop-ecosystem cluster composed of 1 master, 1 DB, and n of slaves, using docker-compose.
- Get experience of hadoop map-reduce routine and hive, sqoop, and hbase system, among the hadoop ecosystem.
Introduction
(1) You’re recommended to use machine with 16GB memory or above. Also, you need linux shell environment with docker and docker-compose V2 installed. (I worked with MacOS system)
(2) Docker images are based on RedHat linux (CentOS 8) with bash shell, which is similar to real-world servers. Open-source versions are like below.
- jdk 1.8.0 (java 8)
- hadoop 3.3.0
- hive 3.1.2
- sqoop 1.4.7
- hbase 1.6.0
- zookeeper 3.6.2
- mariadb 10.5
(3) The reason of using jdk 1.8.0 is hive is not completely supports with jdk11. And hbase with 1.6.0 is used because of the compatibility with sqoop, yet the latest version of hbase is 2.4.2. The latest version is used in other things.
(4) All files related to this practice are in my github. If you’re used to Dockerfile, you can revise the image with Dockerfile in github.
https://github.com/hjben/docker
Sub-folders related on: hadoop-eco, hadoop, zookeeper, mariadb
(5) This practice uses shell script files in folder named by docker-script, where are sub-folder of each folder in github. This shell files get some parameter from user, and then constructs cluster and executes some files needed. docker-compose.yml file also be generated automatically in same path, and deleted when the docker-compose is down.
(6) The docker images are in my docker hub. You can download them with docker pull command.
https://hub.docker.com/search?q=hjben&type=image
(7) MariaDB used in hive and sqoop have similar usage with mysql. It’s open-source version of mysql.
(8) If you have any problems, questions or bugs when using codes, just contact me.
Docker container construction
1. Download docker image
The version of image maybe changed up, with update of the open-source version.
docker pull hjben/hadoop-eco:3.3.0
docker pull hjben/hbase:1.6.0-hadoop3.3.0
docker pull hjben/mariadb:10.5
2. Generate docker container.
(1) Download the shell script in hadoop-eco/docker-script folder at the github and move them to the path where docker commands are available.
(2) With ./compose-up.sh command, docker network and containers are generated. parameters must be entered behind the command with one blank (space-bar) and arranged by the order below. The command will not be executed when lack of number of parameters or wrong input type detected.
- hadoop_version: Version of hadoop (3.3.0 and 3.2.2 are available now)
- (The # of) slaves: The number of hadoop slaves (integer between 1 and 5)
- hdfs_path: Host path for saving hdfs data
- hadoop_log_path: Host path for saving hadoop log
- hbase_log_path: Host path for saving hbase log
- hive_log_path: Host path for saving hive log
- sqoop_log_path: Host path for saving sqoop log
- mariaDB_root_password: Root password of mariaDB (mariadb is recommended)
- mariaDB_data_path: Host path for saving mariaDB data
e.g.
./compose-up.sh 3.3.0 3 /tmp/hadoop /tmp/hadoop_logs /tmp/hbase_logs /tmp/hive_logs /tmp/sqoop_logs mariadb /Users/Shared/workspace/docker-ws/maria-data
(3) There are volumes mounted on host path in each container for logs or data backup. This volumes are used for keep the data when docker containers are broken. Host path must be set with compatibility of your test environment, through some parameters of ./compose-up.sh command. The host paths you’ll use are be made by yourself, preparing when they may not be automatically generated on the host.
(4) Execute ./compose-down.sh command if you want to destroy all containers.
(5) ./compose-up.sh command may mis-correct the generated docker-compose.yml file constructing another containers without compose-down command. So if you want to change the number of hadoop slaves, you’re recommended to run ./compose-down.sh first.
Hadoop
1. Execute hadoop
(1) After the containers are built, Execute the command ./hadoop-start.sh start. Then hadoop service is started in the containers.
(2) In the first time of run hadoop, HDFS volume would be formatted to use them. If you don’t want to format the HDFS volume and just restart the hadoop service, restart parameter has an effect.
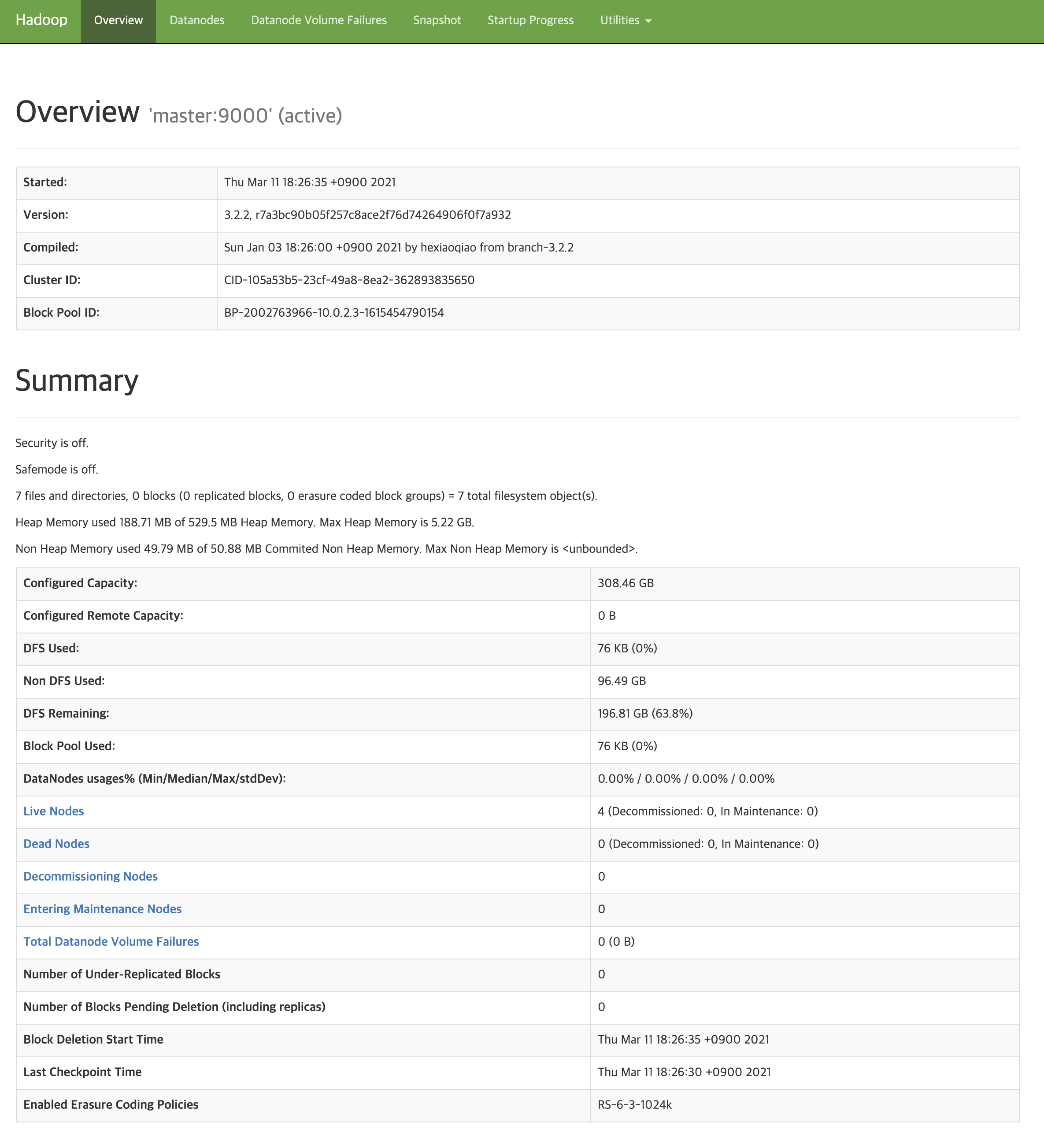
(3) All process are well done, you can access hadoop web ui at the host. addresses for web ui are below.
- job management: localhost:8088
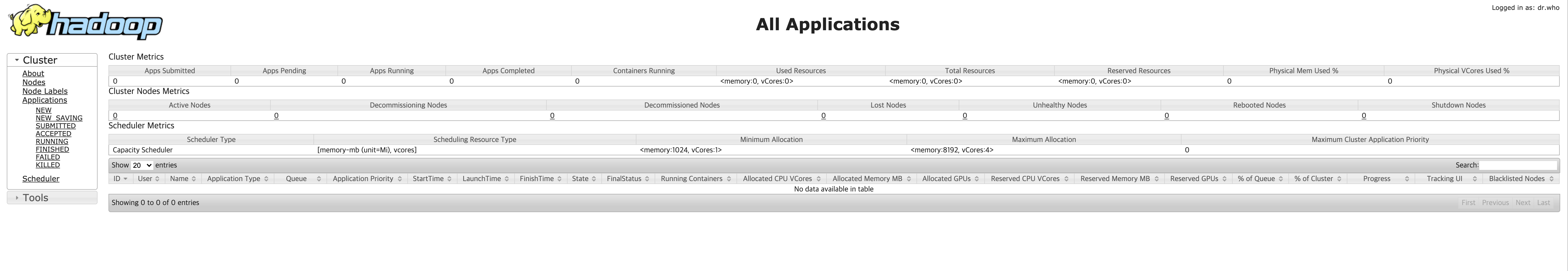
- HDFS management: localhost:9870
- Node management: localhost:8042 (master), localhost:18042 (slave1), localhost:28042 (slave2), …
2. Access to hadoop master shell
(1) CLI used above is occupied by foreground process of hadoop, Open a new CLI(=shell) at host. Then, move into the path docker scripts are in.
(2) Access to the master shell with docker exec -it master bash command. From now on, all tests or practice will be executed on the master shell.
3. Simple test for hadoop map-reduce
(1) You can experience the simple hadoop map-reduce with the command below.
yarn jar $HADOOP_HOME/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-$HADOOP_VERSION.jar pi 2 5
4. Practice for hadoop map-reduce: wordcount
(1) Download and unzip the test data file.
wget https://s3.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/kmubigdata-movielensdata/ml-20m.zip -O /tmp/ml-20m.zip
cd /tmp && unzip ml-20m.zip
(2) Upload the file to HDFS.
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /movies/
hdfs dfs -put /tmp/ml-20m/movies.csvmovies.csv /movies/
(3) Check file in HDFS.
hdfs dfs -ls /movies
hdfs fsck /movies/movies.csv
(4) Set hadoop classpath.
echo "export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=$(hadoop classpath)" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
(5) Build the jar file for wordcount.
cd tmp
mkdir wordcount_classes
javac -classpath $HADOOP_CLASSPATH -d wordcount_classes WordCount.java
jar -cvf WordCount.jar -C wordcount_classes/ .
If WordCount.java file needs, make it with code below.
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class WordCount {
public static class TokenizerMapper
extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable>{
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
}
public static class IntSumReducer
extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "word count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
(6) Run hadoop map-reduce. input is /movies/movies.csv file on HDFS, and output path is /movies/movies_out/.
yarn jar WordCount.jar WordCount /movies/movies.csv /movies/movies_out
(7) Check the result of the map-reduce in the HDFS.
hdfs dfs -ls /movies/movies_out/
hdfs dfs -cat /movies/movies_out/*
(8) Delete the HDFS path you used. (Optional)
hdfs dfs -rm -f -R /movies/movies_out/
Hive
Hive service needs HDFS, so you should execute hive where the hadoop cluster is on. At this time, we’ll use the hadoop cluster made above.
1. Execute hive
(1) Open a new CLI(=shell) at host. Then, move into the path docker scripts are in. Next, start the hive server with ./hive-start.sh all command. The parameter of hive-start.sh file is initalization flag, available values are listed below. It’s first time for running, all parameter is used for total initialization. When the metaDB initialization is on progress, shell asks to you the root password of mariaDB. Then you may pass on mariaDB root password (=mariadb) to the shell.
- meta: Initialize metaDB (mariaDB)
- hdfs: Initialize HDFS path for hive
- all: Initialize both of them.
(2) When initialization is ended, metastore and hiveserver is executed on master. It takes some times for launching hiveserver, and the process is done when you can access the hiveserver web ui. (about.. hive session id is printed 4 times at the CLI)
(3) Web ui address of hiveserver is localhost:10002.
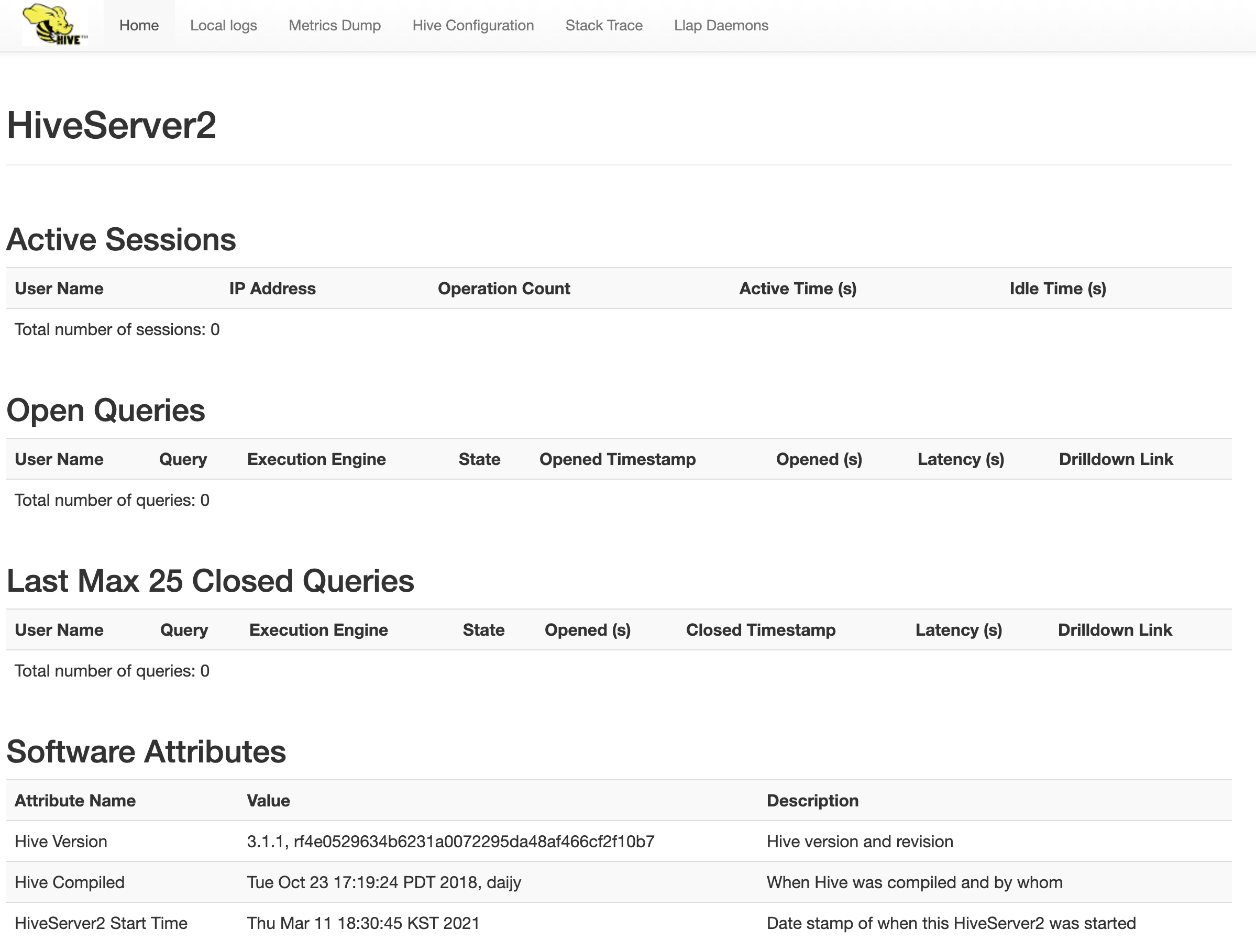
2. Connect to hiveserver with beeline CLI
Beeline is a CLI to connect hiveserver and run some hive commands. It’s bundle of hive installation.
(1) CLI used above is occupied by foreground process of hiveserver, Open a new CLI(=shell) at host. Then, move into the path docker scripts are in.
(2) Access to the master shell with docker exec -it master bash command. From now on, all tests or practice will be executed on the master shell.
(3) Access to the beeline CLI. Set a hiveserver address CLI will connect through -u option.
beeline -u 'jdbc:hive2://master:10000 hive org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver'
3. Create hive table
The hive job command to hiveserver will be executed remotely by beeline. Hive uses hiveQL, which is similar to SQL.
(1) Create a hive database.
create database data;
(2) Create customer table into the database made above.
use data;
create table customer (id bigint, name string, address string);
(3) Insert data into the table. Internal map-reduce process is executed at this time.
insert into customer values (11, "test1", "test1"), (22, "test2", "test2");
(4) Check data in the hive table.
describe customer;
select * from customer;
(5) Use !quit command if you want to exit beeline CLI.
Hbase
Hbase is a NoSQL database executed on HDFS. HDFS is needed by Hbase, so you should execute hive where the hadoop cluster is on. At this time, we’ll use the hadoop cluster made above.
1. Zookeeper cluster construction
Hbase saves their meta information in zookeeper for smooth server management and trouble-shooting. To use hbase, well-working zookeeper service should be exists.
(1) Though there is a mode hbase manages zookeeper directly, Hbase in this docker image uses external zookeeper cluster for a more real-like practice environment.
(2) The way to setting zookeeper cluster is in the post of Kafka cluster. This post assumes there’s zookeeper ensemble cluster in your environment.
2. Execute Hbase
(1) Open a new CLI(=shell) at host. Then, move into the path docker scripts are in. Then, start the hbase master and regionserver server with ./hbase-start.sh all command. The parameter of hbase-start.sh file is initalization flag, If you enter the command with clean flag, it initializes HDFS area hbase would use. If you don’t need initialization, just enter the command without clean flag.
(2) When hbase initialization is done, HMaster is running on master and regionserver on each slave.
(3) Web ui address of hbase master is localhost:16010.
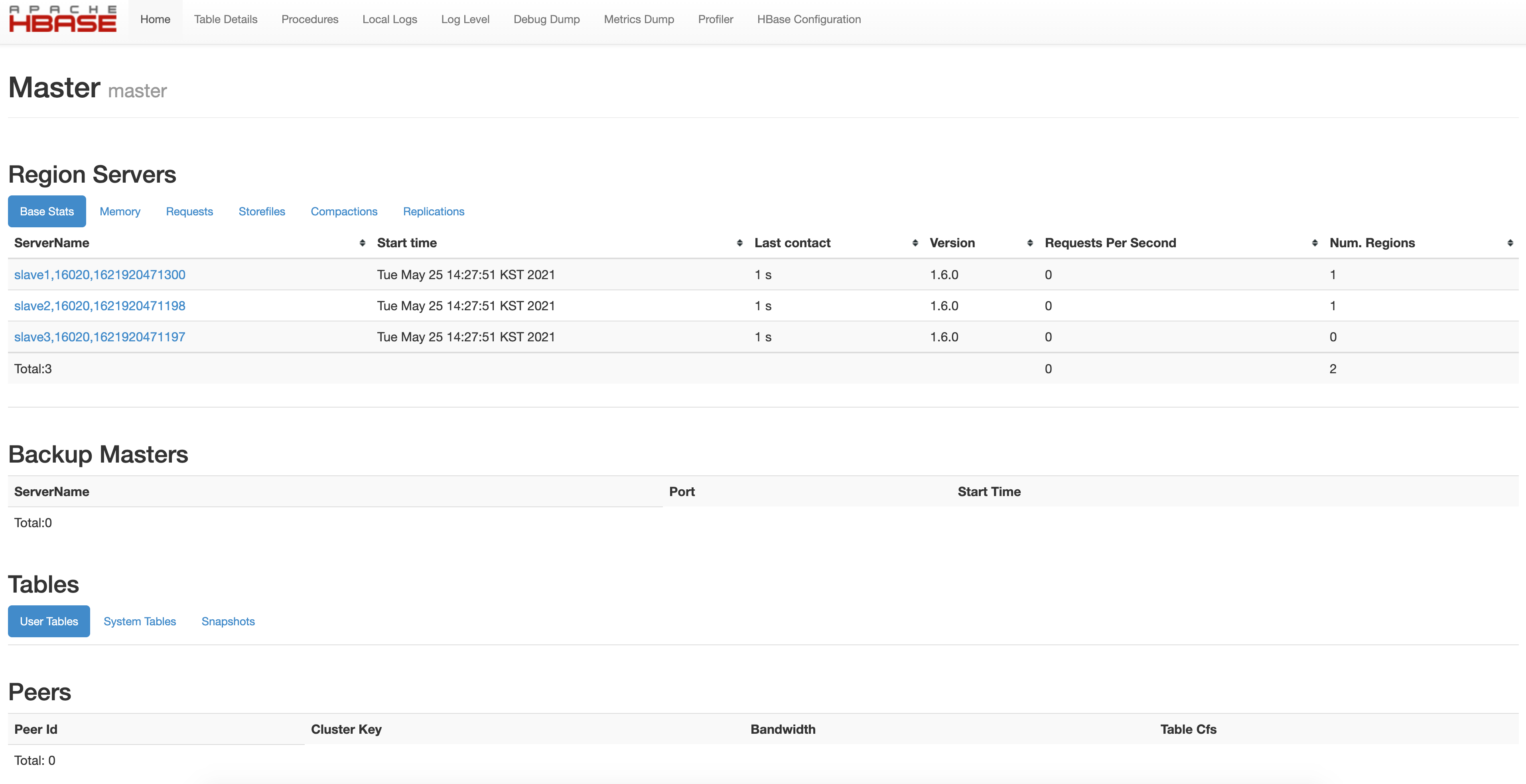
3. Create and delete Hbase data
(1) Open a new CLI(=shell) at host, and access hbase shell with docker exec -it master bash -c “hbase shell” command.
(2) Create a hbase table and check the table list. Hbase table is also be exposed in the hbase web ui.
create 'test', 'data'
list
(3) Insert some sample data in the table.
put 'test', 'row1', 'data:1', 'value1'
put 'test', 'row2', 'data:2', 'value2'
put 'test', 'row3', 'data:3', 'value3'
(4) Check the inserted data.
get 'test', 'row1'
(5) Get all data in the table.
scan 'test'
(6) Delete the table. For deleting table, you should disable them first.
disable 'test'
drop 'test'
list
Sqoop
Sqoop is used for linking Hive, Hbase and RDB data. so you should execute hive where the hadoop cluster is on and we’ll use the hadoop cluster made above.
1. Create sqoop test table in mariaDB
(1) Open a new CLI(=shell) at host and access the mariadb shell with docker exec -it mariadb bash command.
(2) In the mariadb shell, Access the mariaDB database with mysql -u root -p command. The password is already set to when you create the container (maybe mariadb).
(3) Create database and table with SQL.
create database test;
use test;
create table sqoop_test (id int primary key, text varchar(20));
insert into sqoop_test values (1, "test1"), (2, "test2");
2. Execute sqoop (RDB to hive)
(1) Open a new CLI(=shell) at host and access the master shell with docker exec -it master bash command.
(2) Run sqoop hive import. (All contents of sqoop_test in the mariaDB are imported to data.test table in hive)
sqoop import --connect jdbc:mariadb://mariadb:3306/test -driver org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver --username root -P --table "sqoop_test" --target-dir "/user/hive/warehouse/test" --hive-import --create-hive-table --hive-table "data.test"
(3) If all running process is done, You can see the hive table (database: data, table: test).
3. Execute sqoop (RDB to hbase)
(1) Open a new CLI(=shell) at host and access the master shell with docker exec -it master bash command.
(2) Run sqoop hbase import. (All contents of sqoop_test in the mariaDB are imported to test1 table in hbase)
sqoop import --connect jdbc:mariadb://mariadb:3306/test -driver org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver --username root -P --table "sqoop_test" --hbase-create-table --hbase-table test1 --column-family test
(3) If all running process is done, You can see the hbase table (table: test1).